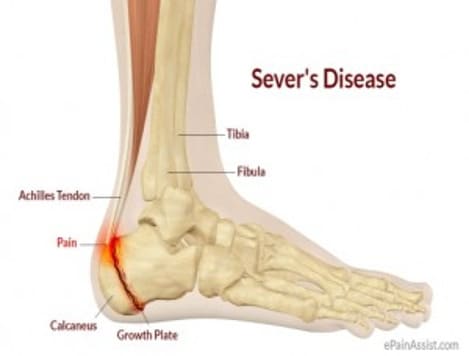
 The most common heel pain in kids is due to Sever’s Disease. Sever’s Disease is an inflammation of the growth plate of the heel bone also called calcaneal apophysitis. The growth plate becomes inflamed when there is too much pull from the achilles tendon and/or the plantar fascia tendon that attaches to the heel bone. This is not a true disease in the sense a child doesn’t have to live with this forever. This generally affects kids between the ages of 8-14 and most commonly in kids who are active.
The most common heel pain in kids is due to Sever’s Disease. Sever’s Disease is an inflammation of the growth plate of the heel bone also called calcaneal apophysitis. The growth plate becomes inflamed when there is too much pull from the achilles tendon and/or the plantar fascia tendon that attaches to the heel bone. This is not a true disease in the sense a child doesn’t have to live with this forever. This generally affects kids between the ages of 8-14 and most commonly in kids who are active.
Does Sever’s Disease Cause Heel Pain in Kids?
Pain in the bottom of the heel is usually due to too much pull of the achilles tendon and/or plantar fascia on the heel bone. When the arches are falling and the plantar fascia is stretched too far, the tendon will pull at its 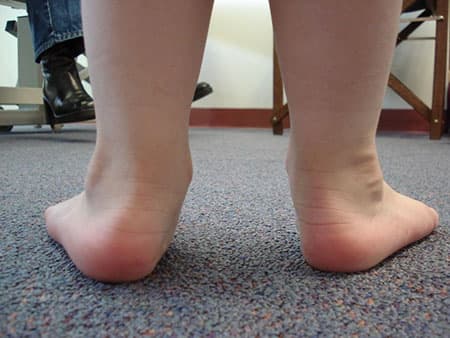 attachment to the bottom of the heel. So with increased activity and with lack of good support in the shoes, the heel becomes inflamed. Another cause of heel pain in kids is simply the bone growing faster than the tendon can keep up with as when the child’s foot is going through a growth spurt. Or if the lower leg is growing- the bone is elongating- and the child is becoming taller, the tendons need to also continue to elongate.
attachment to the bottom of the heel. So with increased activity and with lack of good support in the shoes, the heel becomes inflamed. Another cause of heel pain in kids is simply the bone growing faster than the tendon can keep up with as when the child’s foot is going through a growth spurt. Or if the lower leg is growing- the bone is elongating- and the child is becoming taller, the tendons need to also continue to elongate.
This causes the achilles tendon to pull on its attachment into the back of the heel. Most times during the growth spurt, both the achilles tendon and plantar fascia are needing to elongate and simply can’t keep up. Children with flat feet are more likely to develop Sever’s Disease due to the arch flattening out even more pulling the plantar fascia and the ankle rolling in thus pulling on the achilles tendon on the back of the heel.
What are the Symptoms of Sever’s Disease?
 The most common symptom of Sever’s Disease is heel pain in a child between the ages of 8-14. Usually the pain is worse with activity. The pain can be located on the bottom and/or back of the heel. Sometimes the heel will feel warm due to the inflammation. Oftentimes the pain won’t be present until the activity is over as the tendon tightens up. Pain with the first steps after sleeping or sitting for prolonged periods is also common. As your child compensates for the pain in the heel, some will roll their foot out and start to have ankle pain or ankle instability. Walking on their toes or limiting activity are other ways to compensate for heel pain.
The most common symptom of Sever’s Disease is heel pain in a child between the ages of 8-14. Usually the pain is worse with activity. The pain can be located on the bottom and/or back of the heel. Sometimes the heel will feel warm due to the inflammation. Oftentimes the pain won’t be present until the activity is over as the tendon tightens up. Pain with the first steps after sleeping or sitting for prolonged periods is also common. As your child compensates for the pain in the heel, some will roll their foot out and start to have ankle pain or ankle instability. Walking on their toes or limiting activity are other ways to compensate for heel pain.
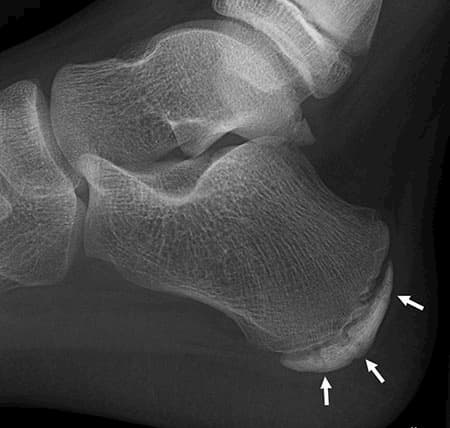
On X-ray the quarter moon area is the growth center. Sometimes the growth center has small cracks as indicated by the arrows and these allow the growth center to grow. Prolonged pain in the heel can lead to an actual fracture in the main body of the heel.
How Do You Treat Sever’s Disease?
1. Arch supports for heel pain.
 The arch support needs to go the full length of the arch runs from the heel to the ball of the foot. Many supports and heel cups may provide some relief but if they end mid arch it is like supporting a bridge at one end of the heel but then only supporting the other end of the bridge part way down, thus the arch will still fall.
The arch support needs to go the full length of the arch runs from the heel to the ball of the foot. Many supports and heel cups may provide some relief but if they end mid arch it is like supporting a bridge at one end of the heel but then only supporting the other end of the bridge part way down, thus the arch will still fall.
When getting an arch support, you must make sure you are getting the support that is for your foot type- average or flat.
J1 insoles for average arches. The arch supports provide 3 point correction in the heel, arch and forefoot.
 Buy Average Arch Support
Buy Average Arch Support
Patented j1 insoles for flat feet. No other over the counter arch support corrects in all 3 areas of the foot like the patented design of j1 insoles for flat feet.
 Buy Flat Feet Support
Buy Flat Feet Support
2. Stretching Exercises for Heel Pain
If the heel is too painful, stretching exercises may irritate the heel and it is advised to hold off on the stretching. Stretching should make the heel feel better not worse.
Calf stretch: To stretch the achilles tendon, stand about 2 feet away from the wall and place your hands on a wall. 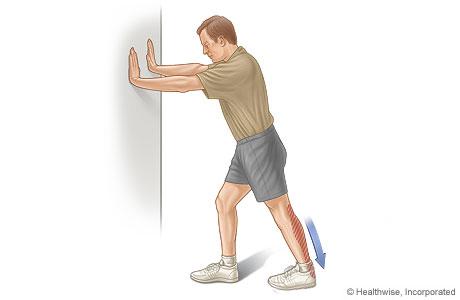 Place one foot behind the other and bend your front knee toward the wall until you feel the back of your heel stretching. Make sure the back foot is straight, not turned outward. While stretching, act like you are squashing a bug with the back of the heel to get maximum stretch of the achilles tendon. To get even more stretch, move your hips towards the front foot and rotate inwards with the hips. Hold the stretch for 15 seconds. Switch your feet and repeat 10 times each side 2-3 times per day.
Place one foot behind the other and bend your front knee toward the wall until you feel the back of your heel stretching. Make sure the back foot is straight, not turned outward. While stretching, act like you are squashing a bug with the back of the heel to get maximum stretch of the achilles tendon. To get even more stretch, move your hips towards the front foot and rotate inwards with the hips. Hold the stretch for 15 seconds. Switch your feet and repeat 10 times each side 2-3 times per day.
Golf ball/tennis ball/frozen water bottle roll: Place a ball on the ground and position the arch of your foot over the ball. Roll your foot in a rotating or forward motion to loosen the fascia located on the bottom of your feet. For a firmer touch, use the golf ball.
Hamstring Stretch: Stand with your feet parallel and straight forward with the feet lined up . While holding onto  the back of a chair lean at the waist. Keep the back and knees straight. Lean down until you start to feel a stretch in the hamstrings (back of the thigh muscles) and then lean the buttocks back getting more of a stretch.
the back of a chair lean at the waist. Keep the back and knees straight. Lean down until you start to feel a stretch in the hamstrings (back of the thigh muscles) and then lean the buttocks back getting more of a stretch.
Another hamstring stretch is sitting in a chair. Make sure the foot is slightly turned in to get the most stretch.
3. Rest, Ice and Anti-inflammatory Medicines
With the heel being inflamed, reducing this swelling will reduce pain. An anti-inflammatory will reduce this swelling and pain. Icing for 15 minutes 2 times per day also helps. It is important to not do any activities that would aggravate the heel and only return to these activities once the pain is all gone or the pain will be prolonged possibly for months.
4. Shoes
Shoes can make the heel pain better or worse and are sometimes the reason someone develops heel pain. Make sure the shoes are lined up in the back. The thickness of the heel needs to be equal on both sides. Many running shoes build up the inside of the heel as compared to the outside and this will cause our heel to tilt outwards. This heel counter also needs to be strong and not easily compressible.
When looking at the bottom of the shoes, make sure the shoe lines up as straight as possible from the heel to the toes. Too much angulation inwards as you get to the toes can also cause the foot to tilt outwards too much.
Proper care of the painful heel(s) with the use of arch supports, stretching, rest, ice and good shoes will generally allow the child to get back to regular activities within a week. If the child returns to the activities too soon, the heel pain can be present for months and may require crutches and/or an ambulatory boot.
When getting an arch support, you must make sure you are getting the support that is for your foot type- average or flat.
J1 insoles for average arches. The arch supports provide 3 point correction in the heel, arch and forefoot.
 Buy Average Arch Support
Buy Average Arch Support
Patented j1 insoles for flat feet. No other over the counter arch support corrects in all 3 areas of the foot like the patented design of j1 insoles for flat feet.
 Buy Flat Feet Support
Buy Flat Feet Support





